
THE ULTIMATE GUIDE TO CLOUD COMPUTING
The cloud is everywhere. Even if we don’t notice, we interact with it. As you check your email in the morning, use your phone maps, watch Netflix, or work with Google spreadsheets, the cloud is there again. Earlier companies needed armies of IT administrators to keep systems updated. Today, with the adoption of cloud computing, businesses can completely automate workflows and increase efficiency.
WHAT IS CLOUD COMPUTING?
Cloud Computing, often referred to as “the cloud,” is a remote virtual pool of on-demand shared resources on a pay-as-you-go basis. With cloud computing, companies become more agile. They modernize and scale their business in ever-changing market conditions. When something is stored in the cloud, that means it’s stored on the Internet instead of physical servers. It’s like having an extra hard drive – one that you can access anywhere and anytime. You need a device that can connect to the internet.
Instead of buying, renting, and maintaining physical data centers and servers, you can access technology services such as computing power, storage, and databases on an as-needed basis from a cloud provider. Cloud computing continues to evolve as a go-to approach for IT, thus eliminating the need to host anything independently. Therefore, it’s no surprise that 75% of organizations stick to a cloud-first strategy.
HOW DOES CLOUD COMPUTING WORK?
To understand how cloud computing works, we need first to distinguish the fundamental components of its architecture. The main parts of cloud computing infrastructure are the front-end part, back-end part, and cloud-based delivery. In a nutshell, the front-end is the part you see, and the back-end is the computing that happens behind the scenes.
The front-end is the visible part the user interacts with. It includes subcomponents that make up the user experience. The front-end cloud infrastructure includes local networks, web browsers, and web applications.
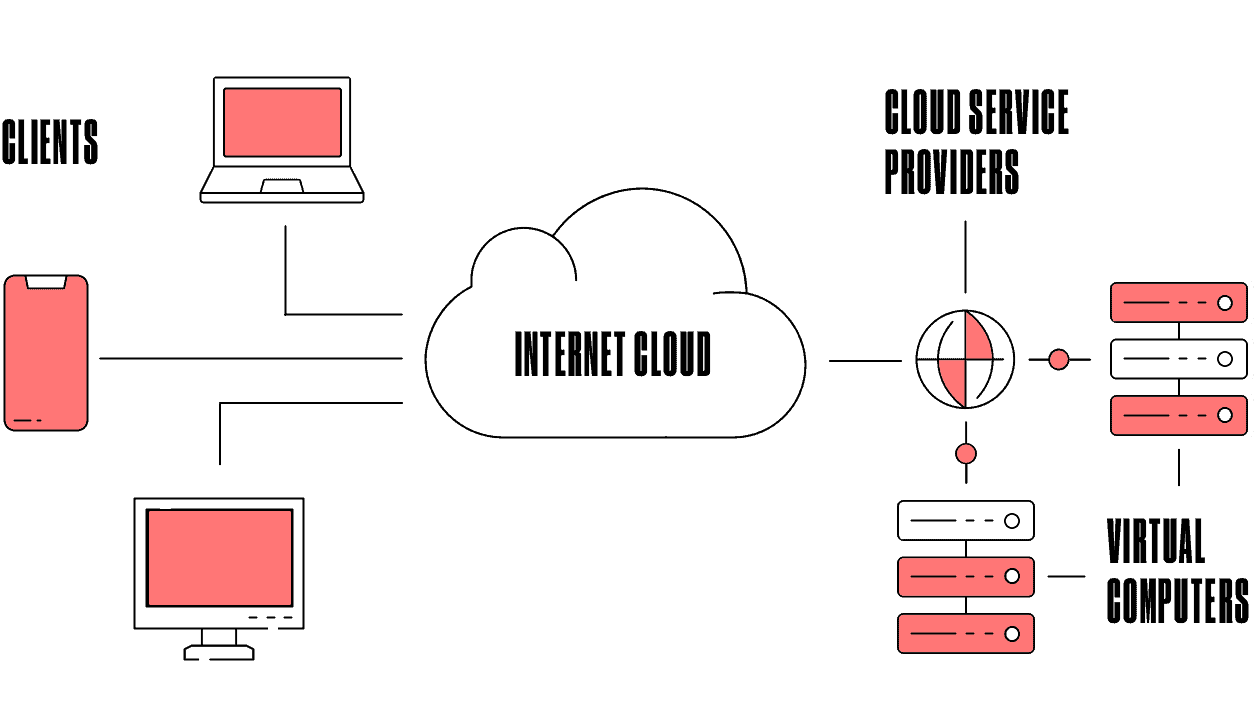
The back-end is the main component of cloud computing. It comprises servers, computers, databases, and central servers. The back-end is responsible for securely storing data.
The front-end and the back-end parts are connected via the network, or in other words, the Internet. Cloud-based delivery is what we offer to the end-users from the cloud via some software, infrastructure, and platforms.
MICROSERVICES IN THE CLOUD
In monolithic architecture, everything is interconnected. If you want to update just one service, the entire system must be updated. As a result, the entire organization can slow down, spending more resources managing the infrastructure that runs this system.
With the advent of Docker and the rise of containers, developers have started to break the monolithic architecture into microservices. The idea behind microservices is that the entire system can be built as a set of services, and each service runs in its own processes and communicates through APIs. The services can be updated and scaled independently under the container infrastructure. This helps to proceed with the cloud transformation journey.
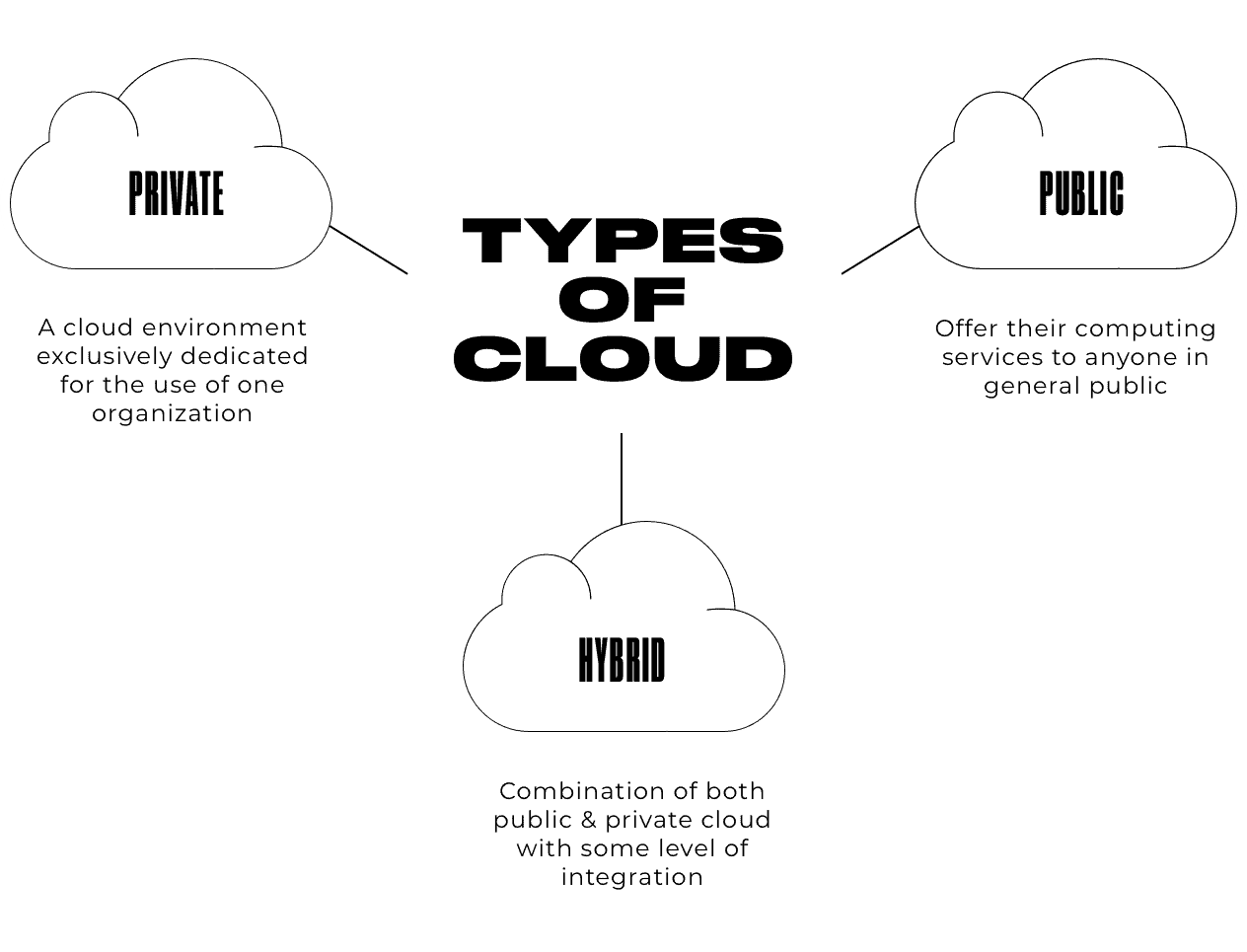
There are three different ways to deploy cloud services: on a public cloud, private cloud, or hybrid cloud.
HOW IMPORTANT IS THE CLOUD?
Cloud computing isn’t just a trendy way to store your photos and videos online. It has already become an integral part of many business models, changing the way these businesses operate. Gartner predicts that half of the global enterprises that use the cloud today will have gone all-in on it by 2021.
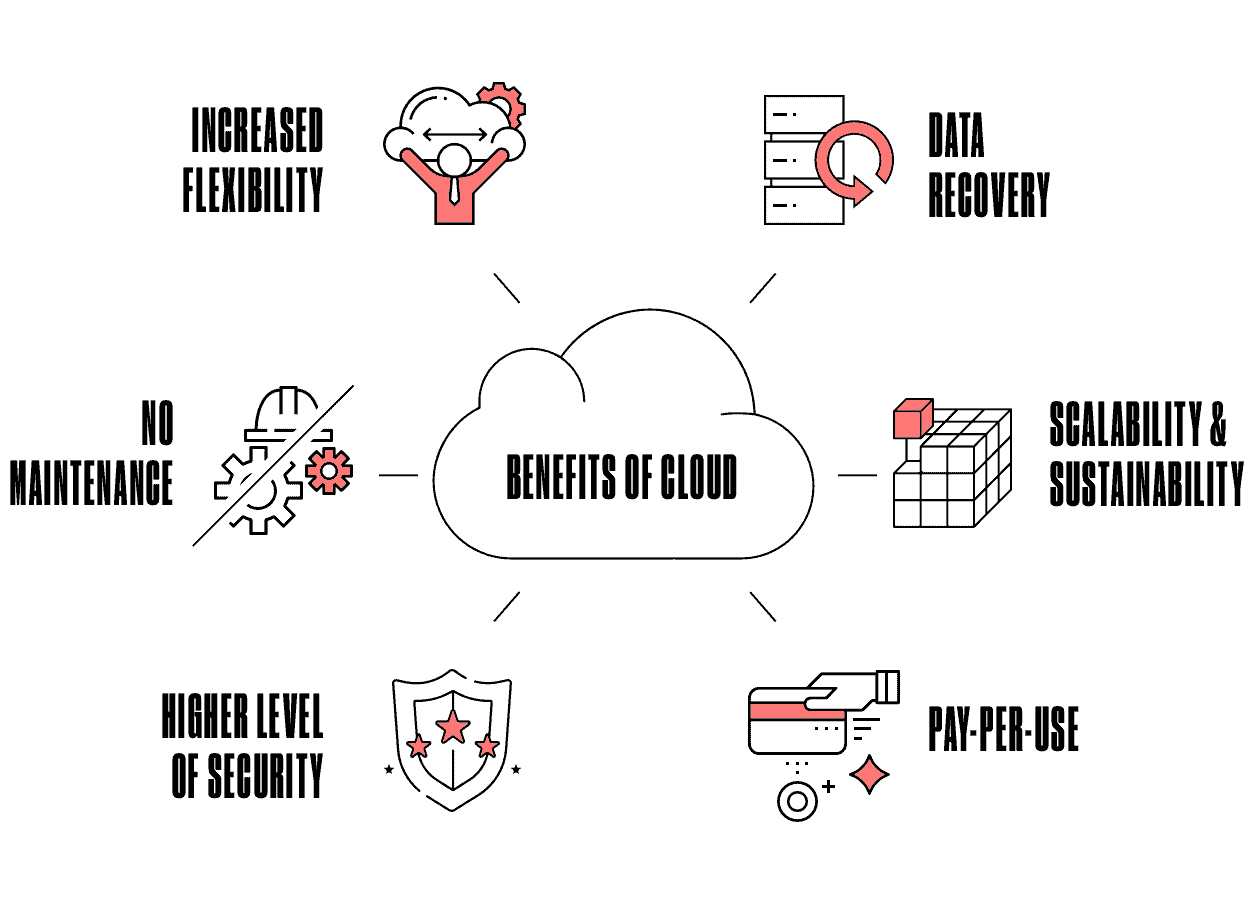
One of the great things about the cloud is that even small and medium-sized operations can benefit from it. Cloud computing is so important because it offers flexibility, data recovery, scalability, easy maintenance, and a high level of security. Besides, with cloud computing, you pay only for your usage. It takes the focus away from having to manage and maintain all the local servers. The cloud moves all that into a hosted environment whereby you have someone else managing it. You only use the service via a web browser, and someone else handles all the back-end processes.
CLOUD COMPUTING ADOPTION
Many companies adopt cloud computing to efficiently manage their applications and data without building and maintaining an on-premise IT infrastructure. Unlike small businesses, large enterprises often find it challenging to migrate their applications to the cloud. Cloud adoption should be not a one-time tactical decision but become a part of the entire strategy to digital transformation.
Netflix is an example of a thoughtful investment in cloud-enabled infrastructure. They spent years transforming and adopting the cloud approach by rebuilding the way their technology operated. Netflix managed to reduce monolithic legacy applications and move to AWS. As a result, service availability has increased, nearing the company’s stated goal of 99.99% uptime and significantly reducing costs.
Most businesses run into the following issues when moving to the cloud:
- The existing platforms were created using the traditional approach. As a result, they are monolithic, and simply moving to the cloud won’t allow them to make use of all dynamic features of the cloud.
- The lack of well-versed in the cloud environment team.
To maximize your chances of successful cloud migration, we suggest following a 12-step cloud migration checklist based on industry best practices.
- Perform a thorough audit of existing IT infrastructure, workflows, tools, and processes.
- Train staff on cloud migration essentials (if needed).
- Identify the existing issues and design solutions for them.
- Create a migration plan.
- Consider potential security risks.
- Confirm that you’ll maintain compliance.
- Project the costs of your cloud migration.
- Design the optimal cloud infrastructure.
- Complete a test project by moving some of the lesser systems.
- Improve the infrastructure based on the test project feedback and outcomes.
- Move the system components to the cloud.
- Configure the CI/CD pipelines.
SUMMING UP
Companies can achieve scalability and efficiency faster by considering cloud computing as a starting point for IT automation. Want to learn more about cloud migration in practice? Read our recent case study for a healthcare provider.
Author
back to all postsOUR RECENT PROJECTS
 REAL-TIME DATA SYNCHRONIZATION
REAL-TIME DATA SYNCHRONIZATION
- productivity app
- debugging
- data synchronization
- offline-first approach
 IMPROVING WEB APP PERFORMANCE
IMPROVING WEB APP PERFORMANCE
- social platform
- customer experience
- container system
- microservices architecture




